First Known Malware Attack Windows Containers
Using Windows Server in a “Windows container”? Then beware of it, as recently, it has been confirmed that highly sophisticated malware has been active for over a year.
The cybersecurity researchers at Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 have recently discovered a new malware, known as, “Siloscape,” and it uses Windows containers to access Kubernetes clusters.
Since they generally focus on Linux systems, that’s why it goes after the Windows containers that are deemed as unusual. To connect to a C2 server that is used by attackers to control the Siloscape, data filtering, and commands, the malware (Siloscape) uses a Tor proxy and an onion domain.
Technical Overview
Through server isolation and un-patched vulnerabilities, Cloudmalware.exe, it’s the malware that targets the Windows containers. After that using the different breakout techniques for Windows containers, Siloscape try to run the RCE on a container’s underlying node.
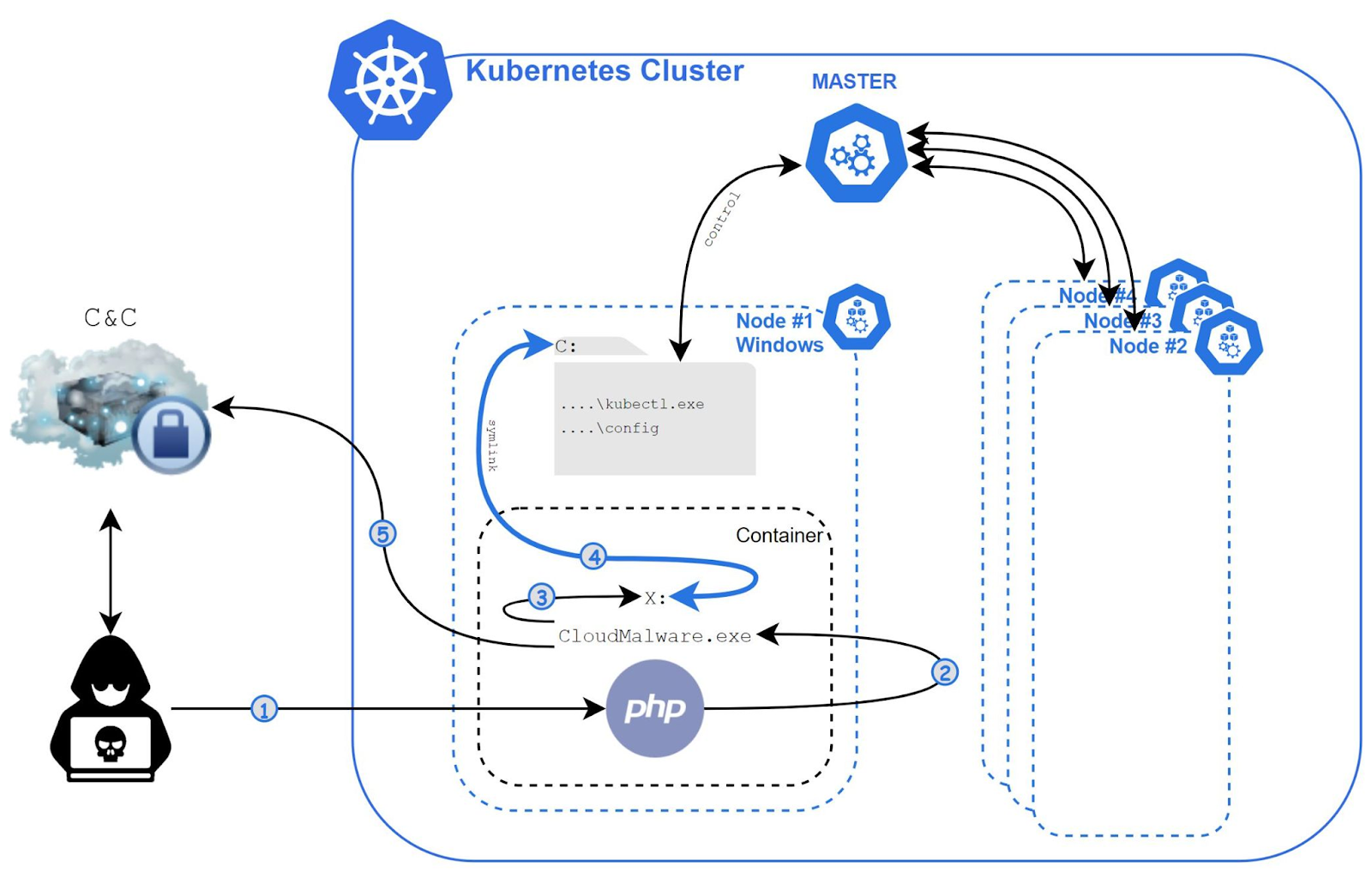
To steal data from the apps present on the cluster or upload cryptographers, the Siloscape will create malicious containers, but these things will be possible when it will manage to break out and establish itself in a cluster successfully.
Behaviors and techniques used
- Exploiting the known vulnerabilities, it targets the common cloud apps for initial access like web servers.
- To gain code execution on the underlying node and avoid the container it uses escape techniques of Windows container.
- To spread in the cluster, it abuses the node’s credentials.
- Over the Tor network using the IRC protocol, it connects to its C2 server.
- While for the further commands, it usually waits.
- Waits for further commands.
During the investigations, the researchers at Palo Alto Networks Unit 42 identified, “23 active victims and a total of 313 victims from the past year.”
However, the security experts were expelled from the server after the operators identified them, and not only that even after their detection they also shut down the service running on the onion address.
Here, initially, the Siloscape evades the detection then it installs a backdoor on the infected system to open the gateway to exploit the negotiated cloud infrastructure to carry out malicious actions like:-
- Theft of credentials
- Theft of personal data
- Ransomware attacks
- Supply chain attacks
Apart from these things, Siloscape has a different view as compared to other malware; since the maximum number of cloud-based malware is designed to carry out DDoS attacks and mine cryptocurrencies.
Indicators of Compromise
| Description | SHA256 |
| Our Siloscape variant | 5B7A23676EE1953247A0364AC431B193E32C952CF17B205D36F800C270753FCB |
| unzip.exe, the unzip binary Siloscape writes to the disk | 81046F943D26501561612A629D8BE95AF254BC161011BA8A62D25C34C16D6D2A |
| tor.zip, the tor archive Silsocape writes to the disk | 010859BA20684AEABA986928A28E1AF219BAEBBF51B273FF47CB382987373DB7 |